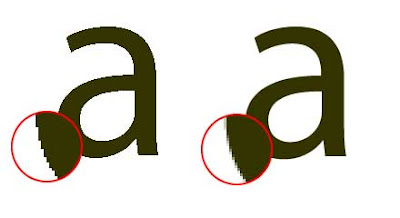
Aliasing is the visual stair-stepping of edges on an image that occurs when an images resolution is too low. Anti-aliasing is when the jagged edges of digital images are smoothed out so there's less distortion by averaging the colours of the pixels at the boundary.
As you can tell from the images they both look the same from a distance however one images is a bitmap image and the other is a vector image. The image on the left that consists of jagged edges is a bitmap image that becomes very pixelated when zoomed in. Whereas the anti-aliased image (on the right) is a vector image which is of a much higher quality and has a lot smoother finish.
The problem with bitmap images is that the image is made up of tiny squares so they never really create a smooth edge. When you zoom into the image these squares just increase in size so the image just looks worse off. As for a vector image your able to anti-alias it, this is when the curve of the image is created with squares of colours that are darker or lighter depending on how much of the curve would take up that square. Anti-aliasing adds shading along the curve to fool the eye into thinking its seeing a smoothed curve rather than a jagged bitmap image.
No comments:
Post a Comment